What Is Left Main Disease
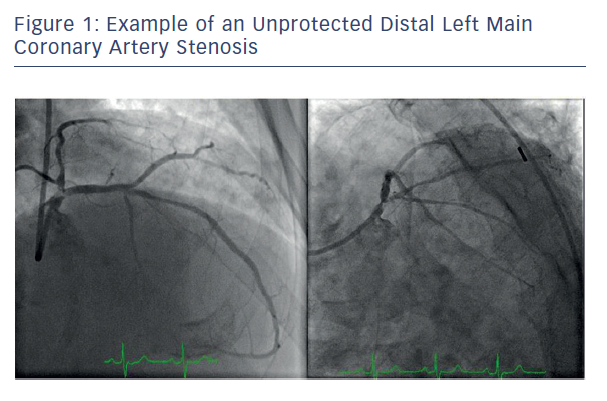
What is left main disease. The optimal management of unprotected left main coronary artery ULMCA disease is currently a debated topic. Unprotected left main disease also called ULMD refers to patients without bypass to the left coronary circulation 2. The advent of coronary angiography in the 1960s allowed for the risk stratification of patients with stable angina.
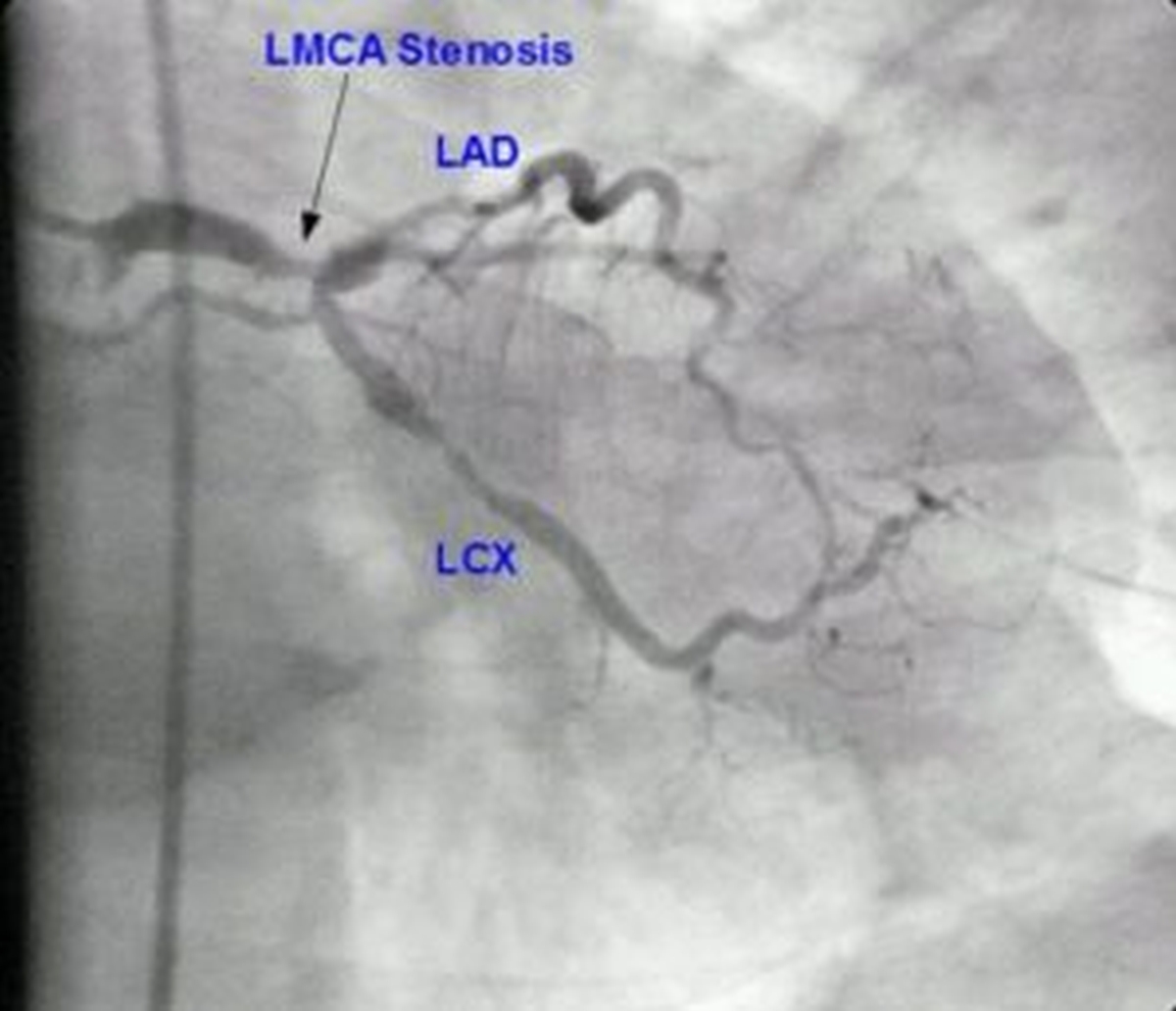
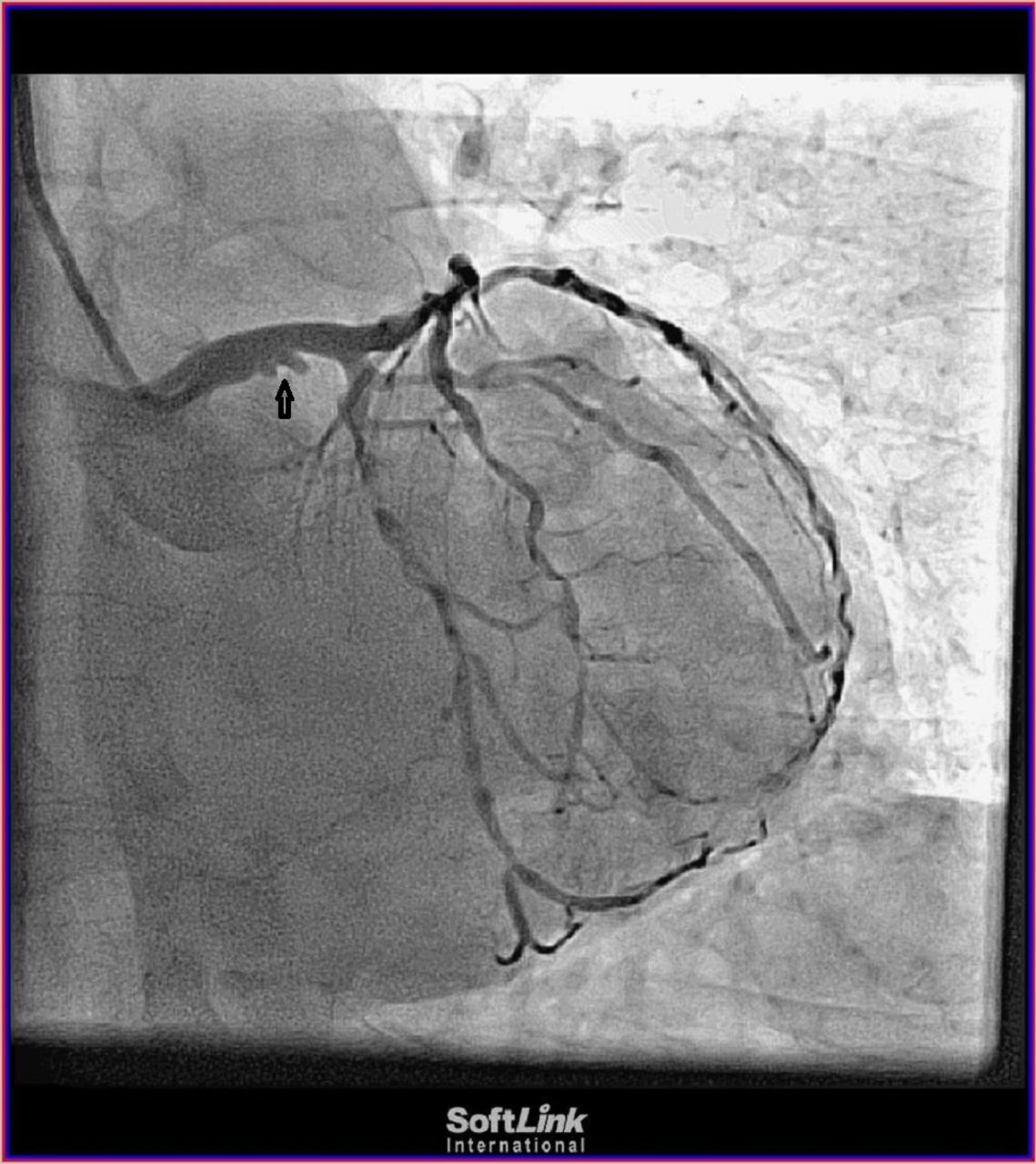
The patients with severe LMS stenosis have a very high risk of major cardiovascular events because of the extent of ischaemic myocardium. It provides oxygenated blood to most of the left ventricle which is the main pumping chamber of the heart. Tapering of the distal left main is also evident in this view.
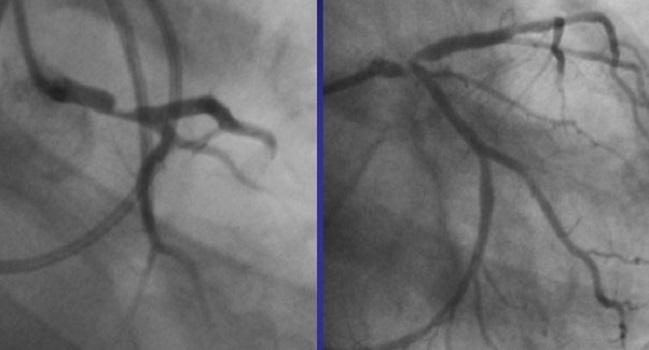
Ostial involvement of LAD is better appreciated in the previous image. Significant left main stem LMS stenosis is amongst the most feared findings during work-up of suspected coronary artery disease. Left main coronary artery disease.
Left main coronary disease is seen in 4-6 of patients undergoing coronary angiography for an ischemic evaluation and is a potentially fatal condition if not promptly identified and treated. Left main coronary artery LMCA stenosis is a relatively infrequent but important cause of symptomatic coronary artery disease. Any amount of blockage in the LMCA such as from plaque buildup or a.
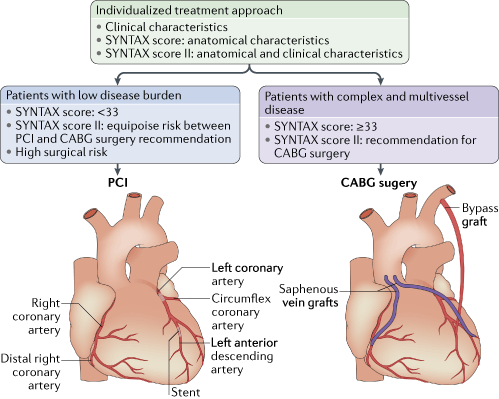
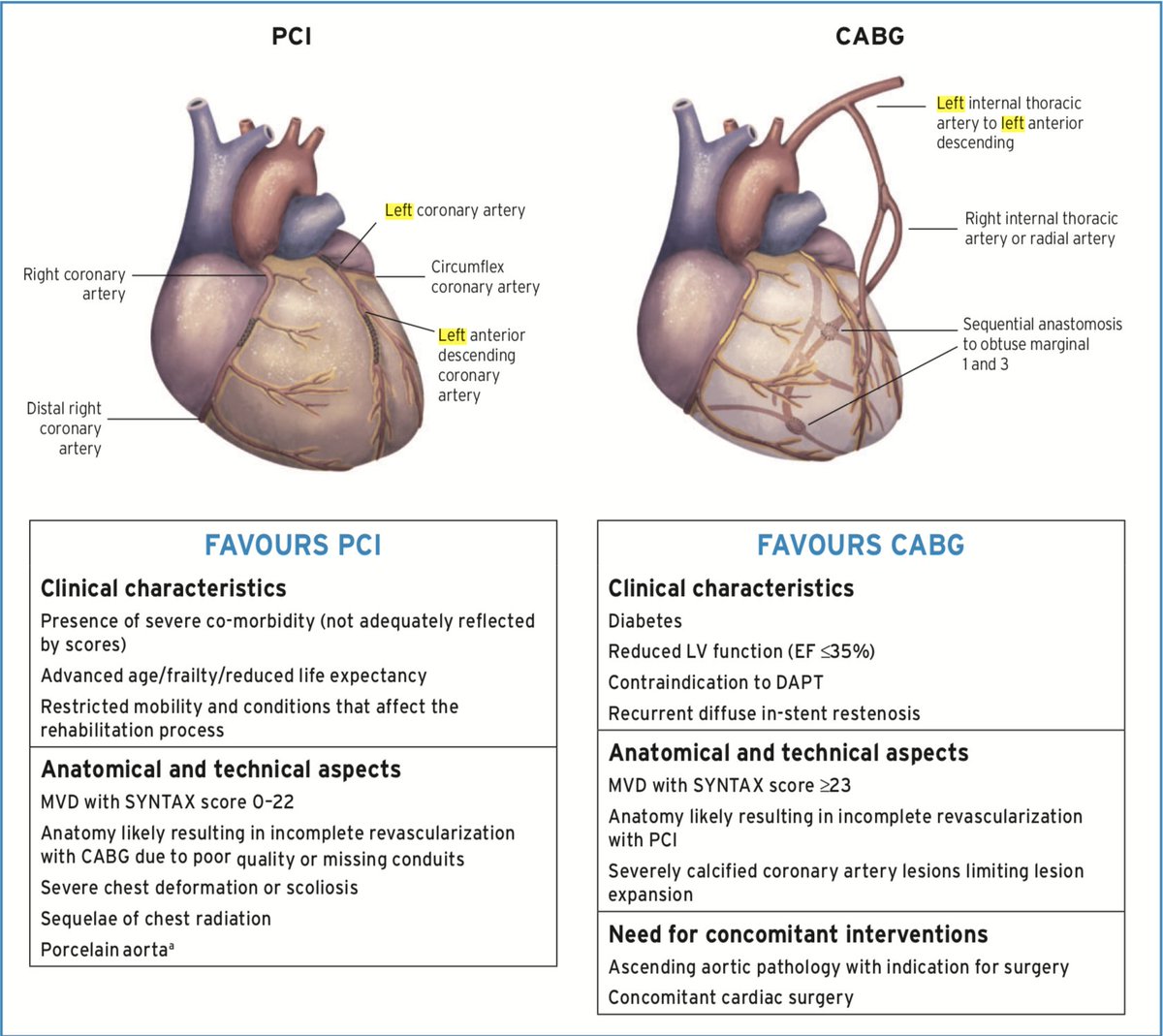
A severe narrowing of the left main coronary artery LMCA jeopardizes a large area of myocardium and increases the risk of major adverse cardiac events. In general there are three options for the treatment of LMCA disease which include optimal medical therapy percutaneous revascularization or surgical revascularization either off-pump or on-pump. Left circumflex coronary artery.
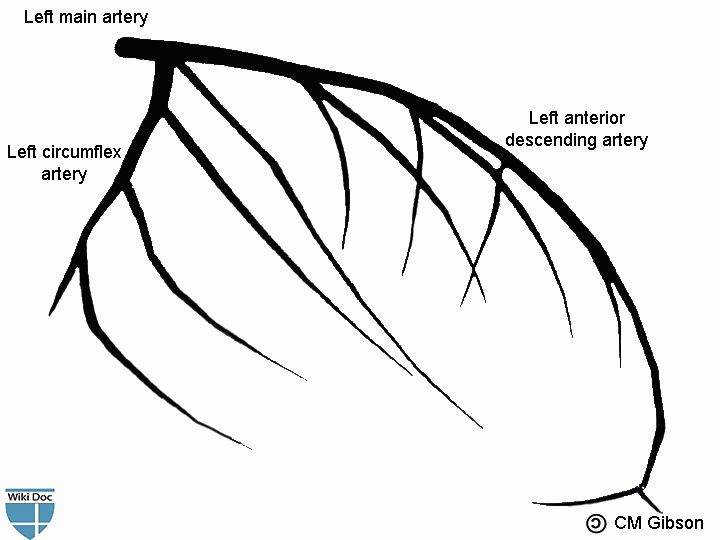
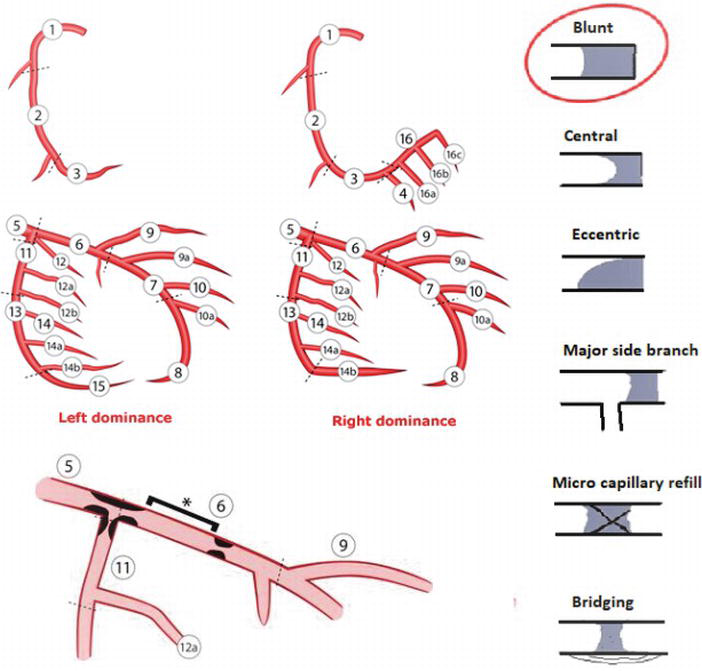
At the level of the junction between the atria and the ventricles the left coronary splits into the circumflex artery which runs to the left. The following are key points to remember from this review article on the management of left main disease. The left main coronary artery LMCA is the very first portion of the left coronary artery.
Left main coronary artery disease LMCAD portends higher prognostic risk as a result of the large myocardial territory at risk ranging from 75 to 100 depending on the dominance of the left coronary circulation. LMCA distal and tight LAD disease RAO caudal view.
At the level of the junction between the atria and the ventricles the left coronary splits into the circumflex artery which runs to the left.
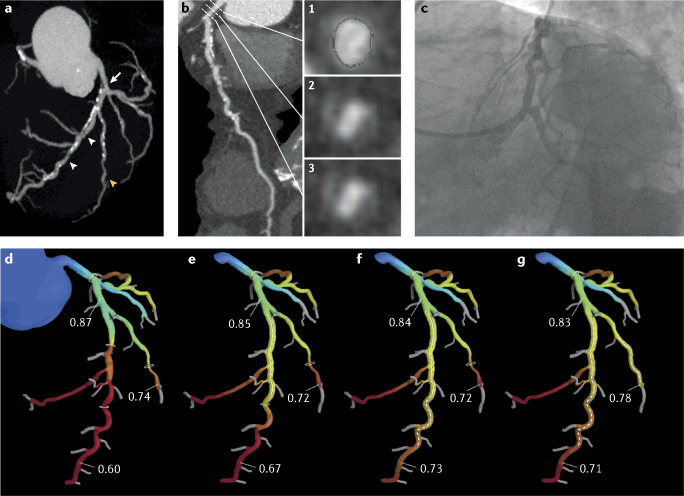
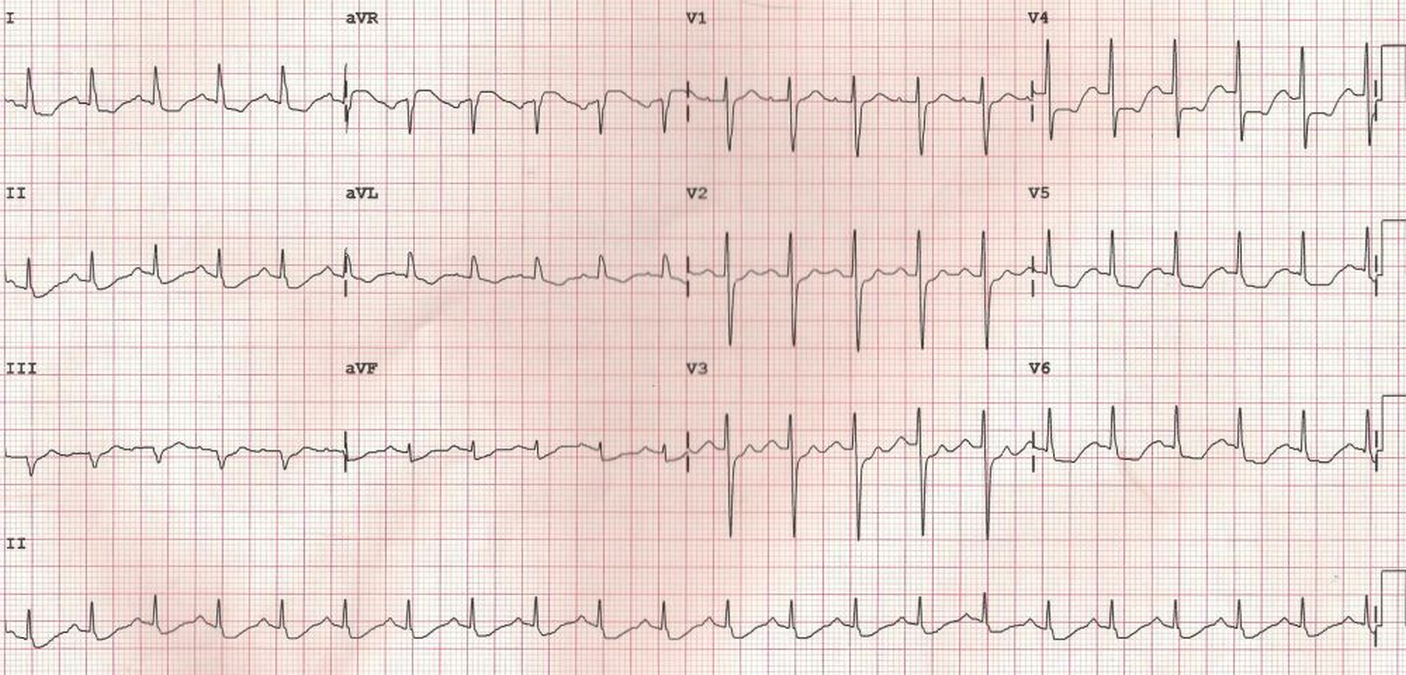
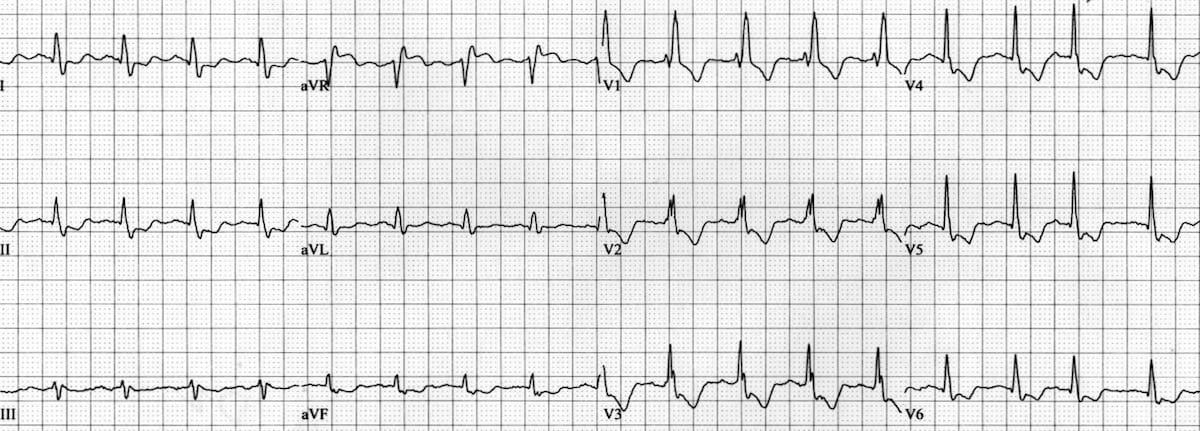
Significant left main stem LMS stenosis is amongst the most feared findings during work-up of suspected coronary artery disease. Recent studies have increased our understanding of the complexity of left main coronary artery disease. Diagnosis and management of significant LMCAD continues to be a source of clinical apprehension and uncertainty. The left main stem subtends a large amount of myocardium and may be associated with ventricular dysfunction arrhythmia or hemodynamic compromise making it a potentially lethal condition. Left main coronary artery LMCA stenosis is a relatively infrequent but important cause of symptomatic coronary artery disease. It provides oxygenated blood to most of the left ventricle which is the main pumping chamber of the heart. It originates from the left aortic sinus a dilation in the aorta just behind one of the leaflets of the aortic valve. Left main diseases usually have extensive coronary artery disease CAD and the coexisting disease is often complex. Left main coronary artery disease.
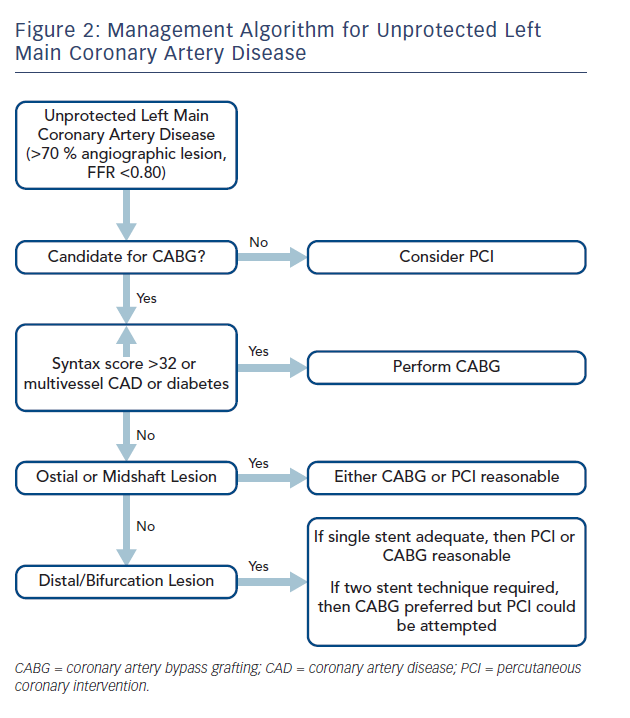
Due its critical location the LMS supplies blood to two thirds of the left ventricle acute occlusion is rapidly fatal and medically managed LMS disease carries a poor prognosis with a one year mortality of approximately 201. The optimal management of unprotected left main coronary artery ULMCA disease is currently a debated topic. The following are key points to remember from this review article on the management of left main disease. Significant left main coronary artery disease is defined as a greater than 50 angiographic narrowing of the vessel. Percutaneous coronary intervention PCI has seen an increased adoption for the management of ULMCA disease after numerous small-scale randomised trials and cohort studies showed equipoise with coronary artery bypass grafting CABG for low complexity lesions. One of the two main epicardial arteries that feed the heart muscle. 1 Multiple studies have found LMCA stenosis to be an independent indicator of increased morbidity and mortality rates among patients with coronary artery disease.


























Posting Komentar untuk "What Is Left Main Disease"