Systemic Sclerosis Lung Disease
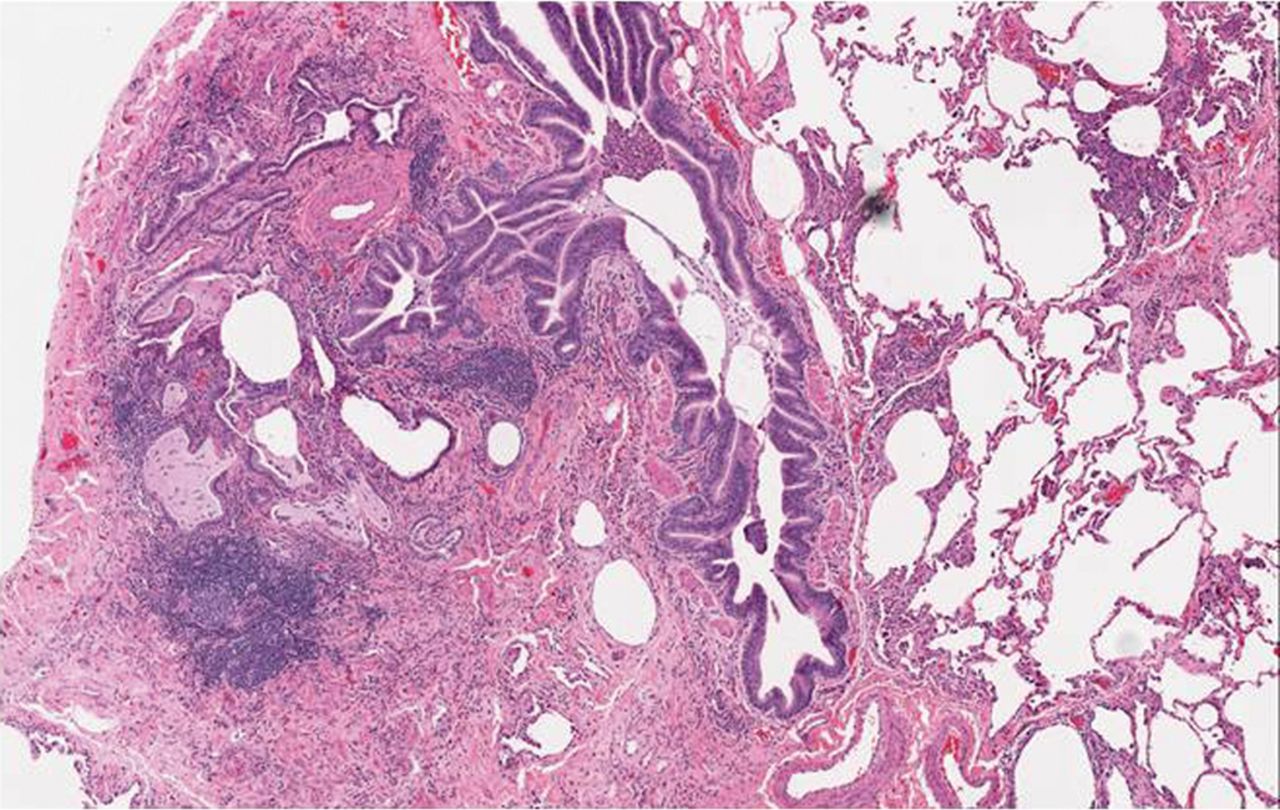
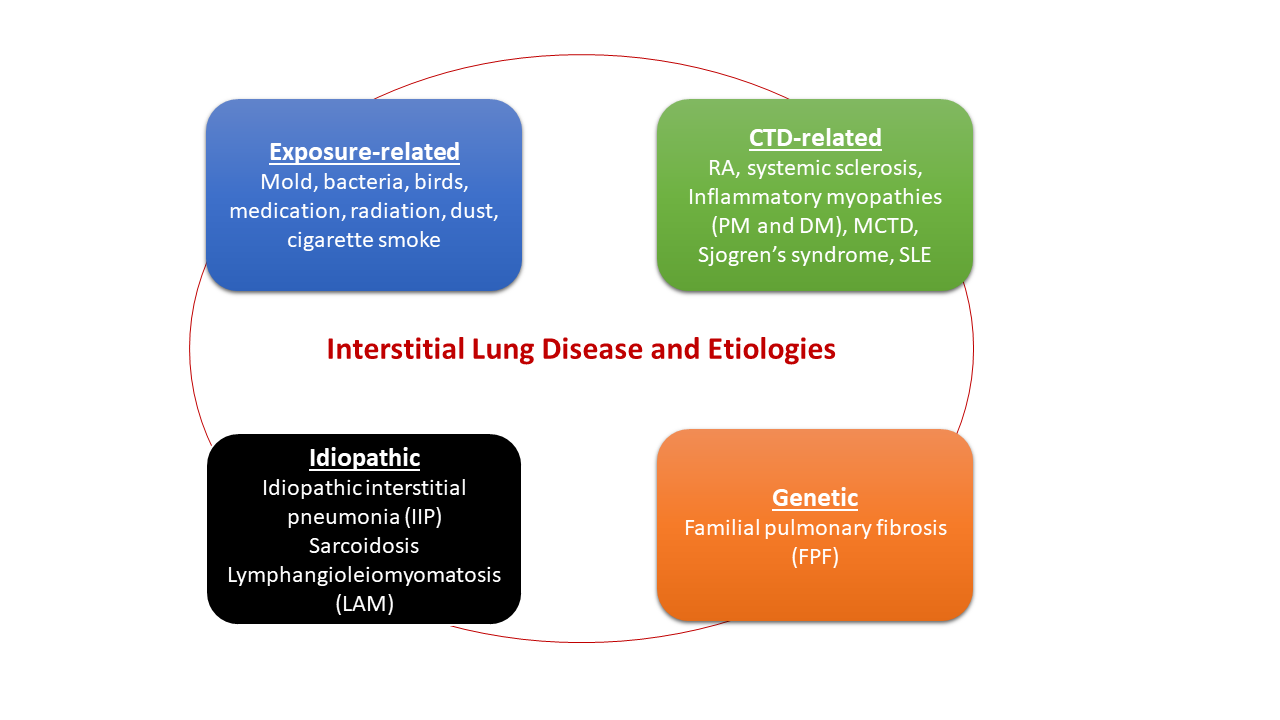
Systemic sclerosis lung disease. Systemic sclerosis SSc is a systemic autoimmune disease that is characterised by endothelial dysfunction resulting in a small-vessel vasculopathy fibroblast dysfunction with resultant excessive collagen production and fibrosis and immunological abnormalities. Systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease accounts for up to 20 of mortality in these patients and has a highly variable prognosis. Although ILD remains the major cause of death in these individuals there is no consensus statement regarding the classification and characterization of SSc-related ILD SSc-ILD.
More than 40 of patients with SSc show evidence of interstitial lung disease ILD. Three steps are considered to be involved. There are two major subgroups of systemic sclerosis based on the extent of skin involvement.
Systemic sclerosis SSc is a rare disease that affects about 25 million people worldwide. Clements Anna-Maria Hoffmann-Vold Daniel E. Approximately 80 of SSc patients may be affected by interstitial lung disease ILD a progressive disease that can significantly impact lung function and can be life-threatening.
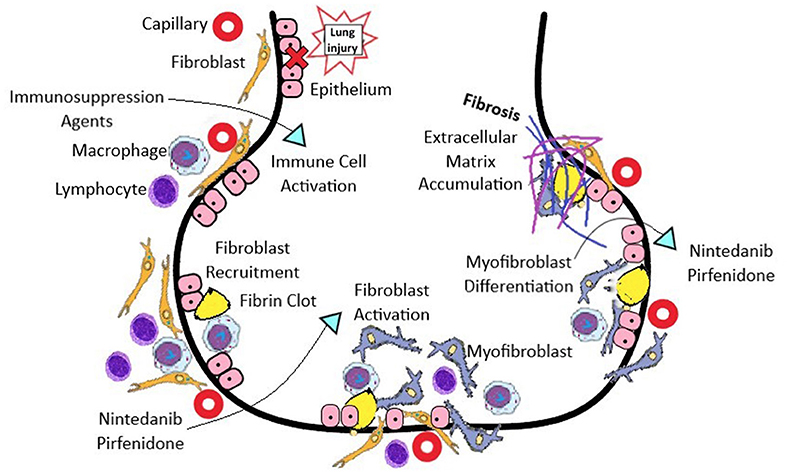
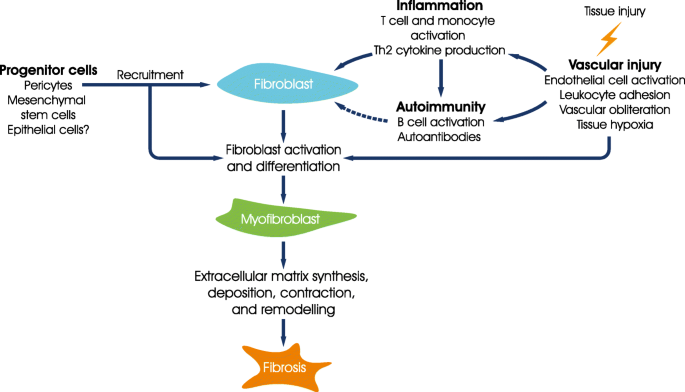
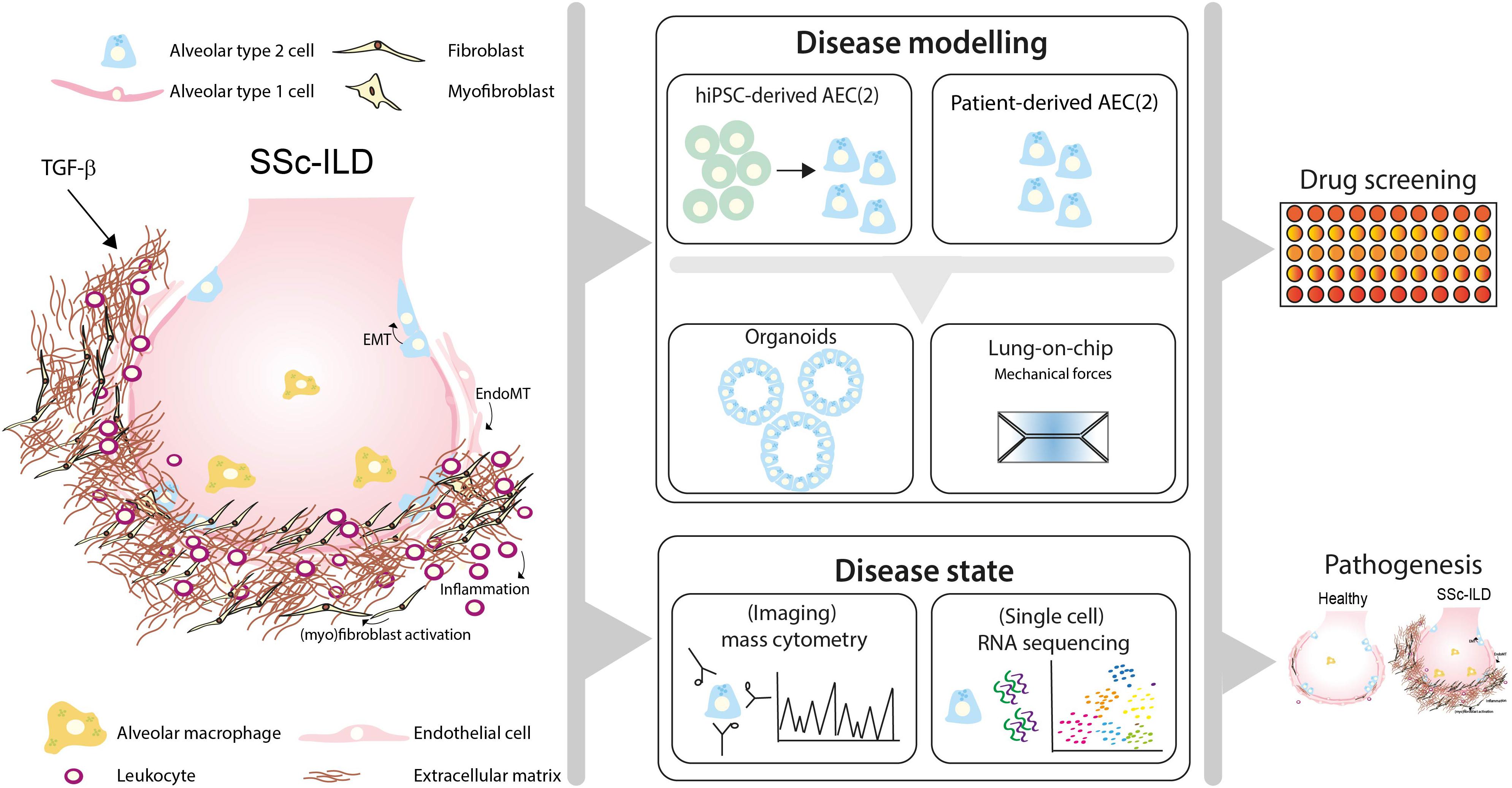
Unlike the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias survival of patients with NSIP. Systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease is the end result of the interplay between fibrosis autoimmunity inflammation and vascular injury. The epidemiology of SSc and SSc with ILD SSc-ILD in the United States varies based on different methodologies used.
Tashkin Myung Sim Ning Li Dinesh Khanna Michael D. Furst Grace Kim Jonathan Goldin and Robert M. Where do we stand.
Cyclophosphamide for Systemic Sclerosis-related Interstitial Lung Disease. Functional respiratory imaging a quantitative computed tomography imaging technique that allows mapping of regional information can provide a detailed view of lung structures. Nintedanib a tyrosine kinase inhibitor has been shown to have antifibrotic and antiinflammatory effects in preclinical models of systemic sclerosis and ILD.
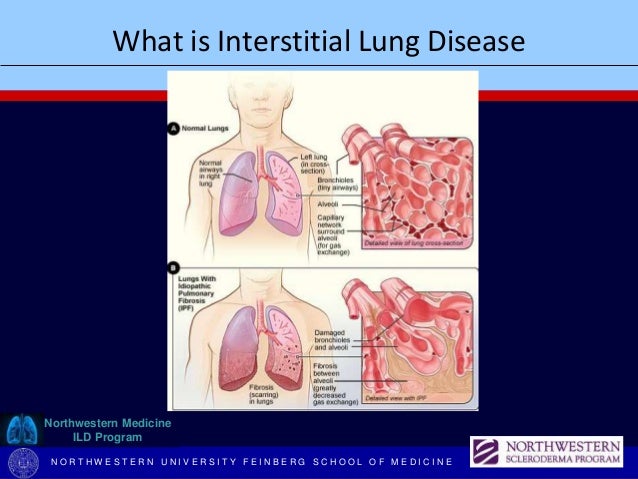
Systemic sclerosisassociated interstitial lung disease remains a leading cause of mortality. Systemic scleroderma or systemic sclerosis is an autoimmune rheumatic disease characterised by excessive production and accumulation of collagen called fibrosis in the skin and internal organs and by injuries to small arteries.
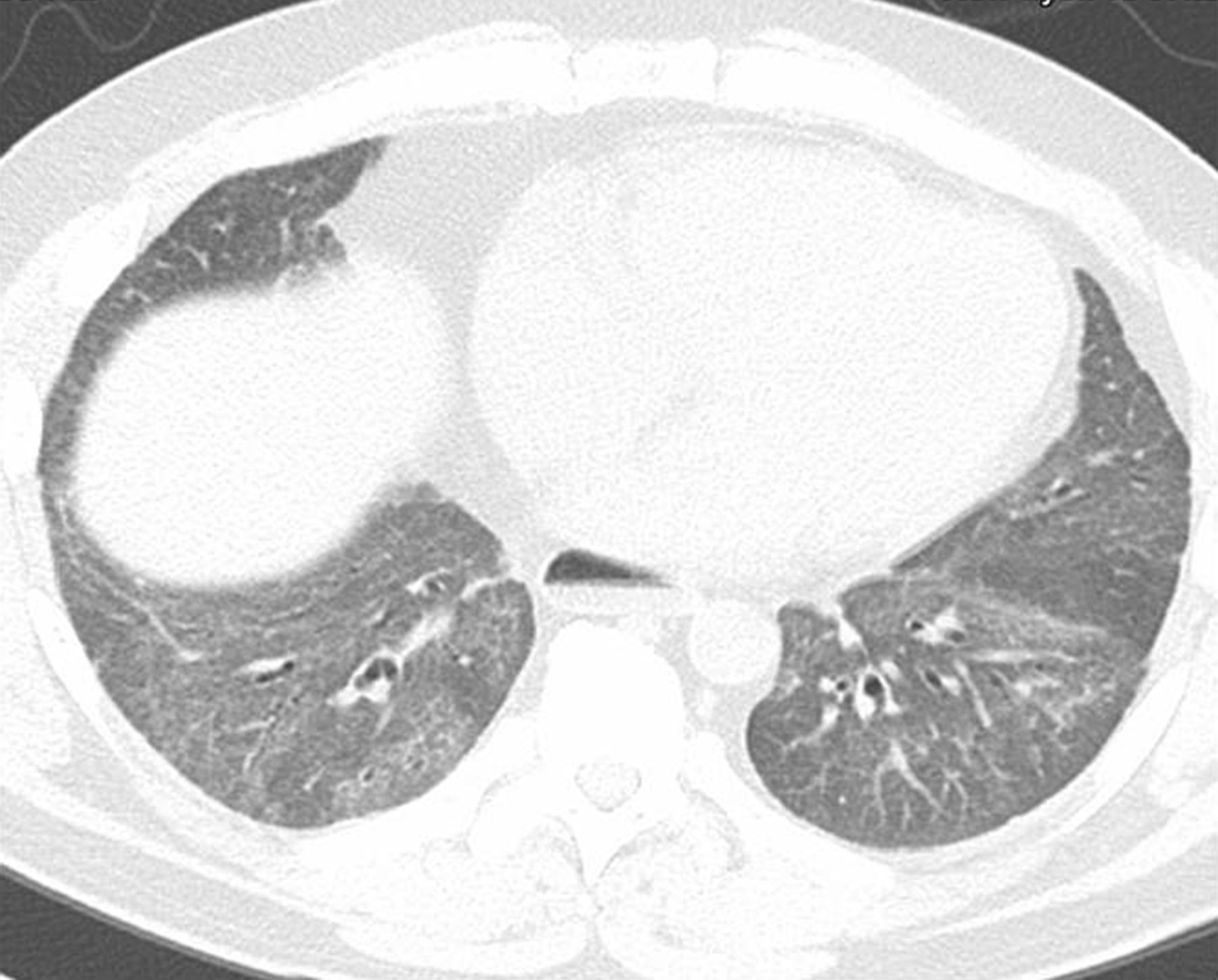
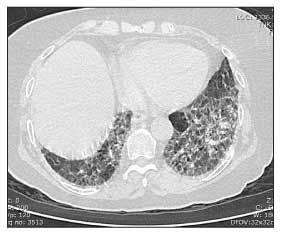
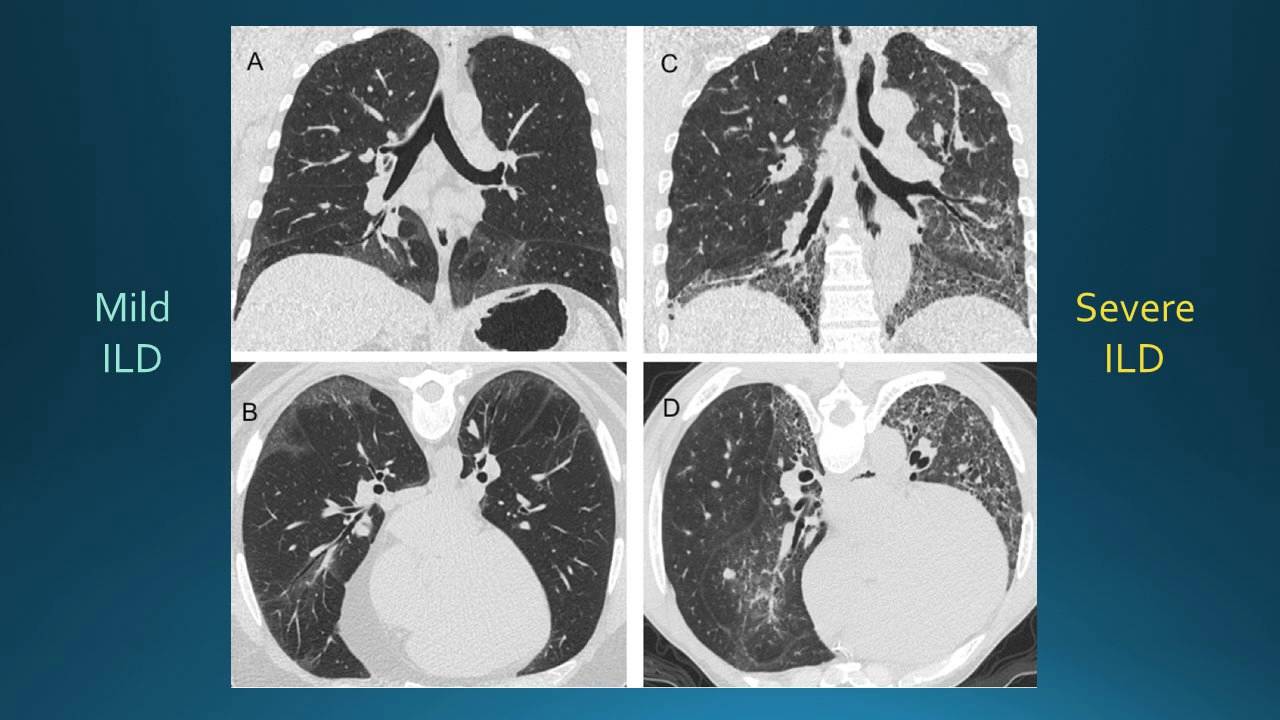
Systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease most commonly presents with dyspnoea cough and a non-specific interstitial pneumonia pattern on CT scan with a minority of cases fulfilling the criteria for usual interstitial pneumonia.
Systemic sclerosisassociated interstitial lung disease remains a leading cause of mortality. A subgroup of patients with systemic sclerosis SSc develop interstitial lung disease ILD characterized by inflammation and progressive scarring of the lungs that can lead to respiratory failure. Systemic sclerosis SSc is a systemic connective tissue disease. Systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease is the end result of the interplay between fibrosis autoimmunity inflammation and vascular injury. More than 40 of patients with SSc show evidence of interstitial lung disease ILD. Systemic sclerosis SSc is a rare disease that affects about 25 million people worldwide. Systemic sclerosis SSc has the highest cause-specific mortality of all of the connective tissue diseases 1. With the recent completion of the SENSCIS study there is now a paradigm shift in the management of systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease that includes the addition of nintedanib to standard immunosuppressive therapy. Unlike the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias survival of patients with NSIP.
The limited form affects areas below but not above the elbows and. The analyses presented at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology aim to improve current prognostic abilities in patients with systemic sclerosisinterstitial lung disease. Unlike the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias survival of patients with NSIP. Tocilizumab has demonstrated lung function preservation in two randomized controlled trials in early systemic sclerosis SSc. Systemic sclerosis SSc has the highest cause-specific mortality of all of the connective tissue diseases 1. Lung disease in SSc Lung disease including interstitial lung disease and pulmonary hypertension can begin in early or late disease. A subgroup of patients with systemic sclerosis SSc develop interstitial lung disease ILD characterized by inflammation and progressive scarring of the lungs that can lead to respiratory failure.































Posting Komentar untuk "Systemic Sclerosis Lung Disease"